Research and Development
Research and development activities in the Group again concentrated on two areas in 2013: expanding its product portfolio and improving the functionality, quality, safety and environmental compatibility of our products.
Focus of our research and development activities
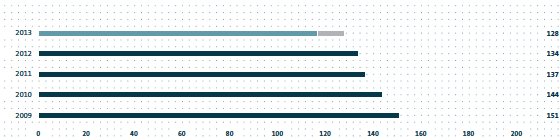
We plan to cut the average CO2 emissions of the Volkswagen Group’s new European passenger car fleet to 120 grams per kilometer by 2015. We have already succeeded in reducing CO2 emissions over the past five years by 23 grams of CO2 per kilometer to 128 grams of CO2 per kilometer. Since 2012, the CO2 emissions for vehicle
CO2-EMISSIONS OF THE VOLKSWAGEN GROUP'S EUROPEAN (EU 28) NEW PASSENGER CAR FLEET
in grams per kilometer
A focus of the Technical Development function in 2013 was on continuing to roll out the Modular Transverse Toolkit. After the first models to be based on the Modular Transverse Toolkit – the Audi A3, the new Golf and the SEAT Leon – were launched in the market in 2012, further derivatives of these models followed during the reporting period, as well as the new ŠKODA Octavia. Other vehicles, such as the Golf Sportsvan that has already been unveiled, will follow.
Automatic driving functions promote predictive driving and offer the potential for increasing efficiency. They make steering safer by reducing the probability of human error, and increase comfort. They also enhance the flow of traffic, thus contributing to the better use of infrastructure. In the near future, a roadworks assistance function will help to reduce or completely avoid accidents around roadworks, for example. We are also conducting research into highly and fully automated driving.
Another focus of our research and development in the past year was on mobile online services. These promote comfort, safety and traffic efficiency and support the vision of cooperative, environmentally friendly and accident-free driving. Volkswagen’s Group Research function proved that these technologies are practicable in the grant-assisted project it completed in mid-2013 entitled “Safe and Intelligent Mobility Test Field Germany” (simTD). The first elements we tested were warnings about danger zones and the ends
of traffic jams, intervention by active safety systems and information about traffic light phases.
When it comes to our ambitious target to reduce CO2 emissions, lightweight construction for large series is becoming increasingly important. The cooperation between Group Research and the production and components departments is accelerating research into lightweight construction and its future production technologies within the Group. Since 2012, we have also been researching economical lightweight construction technologies as part of the public-private partnership “Open Hybrid LabFactory” in collaboration with the Lower Saxony Research Center for Vehicle Technology (NFF) at the Technical University of Braunschweig and other industry partners. We agreed on a contractual framework in 2013 and established the focuses of our research and technology activities. The aim is to have around 200 researchers from industry and science jointly developing hybrid lightweight structures by the end of 2015.
We are constantly extending the use of virtual technologies in our processes, so as to speed up and improve the vehicle development, production, or service process. Smartphones play an increasingly key role in this. The primary focus is on augmented reality technology, in which the real world is recognized and enriched with virtual information. The Audi brand already employs this technology, and Volkswagen is making use of it for the first time in the XL1. Further applications are being developed by Volkswagen’s Group Research function. In addition, Volkswagen uses virtual technologies to improve the ergonomics of work sequences in production, for example.
Recognizing new developments in society, technology, politics, the environment and the economy at an early stage is an important basis for innovations and business success. This is why Group Research constantly addresses the latest social and technological trends. It has established interfaces to key global automotive markets to do this. Research offices in China, Japan and the USA
observe technological areas relevant to the automotive industry, conduct cooperative projects with research institutions and local companies, and thus capture new data for the Volkswagen Group.
Innovations incorporated into vehicles
The “Automotive INNOVATIONS Awards” are presented every year to vehicle manufacturers by the Center of Automotive Management, an independent organization that conducts empirical research on automobiles and mobility. In fiscal year 2013, the Volkswagen Group won in the “Most Innovative Automotive Company”, “Best Manufacturer: Conventional Drives”, “Best Manufacturer: Alternative Drives” and “Best Manufacturer: Connected Car” categories, once again underscoring its innovative power.
The following are some examples of our innovations in the past fiscal year:
The innovative highlight for the Volkswagen Passenger Cars brand was the XL1, produced in a limited run. With a drag coefficient of 0.189, it is the most aerodynamic series vehicle in the world. Thanks to high tech lightweight construction, it weighs just 795 kg. The XL1 emits only 21 grams of CO2 per kilometer and consumes just 0.9 l of diesel per 100 km with its plug-in hybrid system, consisting of a two-cylinder TDI engine with 35 kW (48 PS), an electric motor with 20 kW and a seven-speed direct shift gearbox (DSG). This also makes it the world’s most economical series automobile with a combustion engine.
The e-up! was launched in 2013 – our first vehicle with a purely electric drive. Its 60 kW (82 PS) electric motor, in combination with an 18.7 kWh lithium-ion battery, gives it a range of up to 160 km. The e-up! can be charged using a 230 volt electric socket, a wall box installed on the customer’s premises, a public AC charge point, or via a DC fast charging station featuring the combined charging system (CCS), which charges the vehicle up to 80% within just 30 minutes.
The Audi brand presented the first notchback model in the compact premium segment with the A3 saloon in the reporting period. Fitted with a 1.4 TFSI engine and the new cylinder-on-demand technology, the vehicle consumes only 4.8 l per 100 km and emits 111 g/km of CO2. In addition, this new member of the A3 family not only features a low weight thanks to its lightweight construction, but also a large number of high-end infotainment and driver assistance system solutions.
In our new Audi A8, we are using Matrix LED technology for the first time, which sets new standards for headlights in terms of design and technology: the high beam headlights are divided into 25 individual segments whose light-emitting diodes can be separately switched on and off or dimmed depending on the situation. This allows the system to respond to other vehicles with great precision. The headlights also offer intelligent curve lighting, new-look daytime running lights and indicators with dynamic signaling.
Porsche proved its expertise in hybrid technology in 2013: the Panamera S E-Hybrid is the first plug-in hybrid in the luxury class. With its 416 PS combined maximum output, the E-Hybrid accelerates from 0 to 100 km/h in 5.5 seconds. Its top speed is 270 km/h. In purely electric mode, the Panamera S E-Hybrid travels 36 km, with a top speed of 135 km/h. The vehicle uses an average of just 3.1 l of fuel per 100 km, corresponding to CO2 emissions of 71 grams per kilometer. It also offers an entirely new range of comfort functions, which can also be activated and accessed via a smartphone app. These include the display for the battery’s charge status and range, preheating or precooling the vehicle, and guiding the driver to the parked vehicle.
The Porsche 918 Spyder is ringing in a new era in sports car manufacturing. Designed as a high-performance hybrid from the ground up, it marries the performance of a super sports car with the virtually silent drive of an electric vehicle. Its combined maximum output of 652 kW (887 PS) catapults the hybrid from 0 to 100 km/h in 2.8 seconds. When the vehicle is started, the “E-Power” mode is activated as standard if the battery charge level is sufficient.
Scania Streamline is responsible for the new long-distance models of the G and R ranges, which are optimized for low fuel consumption. Alongside improved aerodynamics and a complete air deflector package, a new version of the Scania Opticruise transmission contributes to this. The economy mode is fully integrated into the Scania Active Prediction predictive cruise control. Combined with the new generation of Euro 6 engines, up to 8% of fuel can thus be saved in long-distance driving.
MAN successfully launched the series production of Euro 6 technology for trucks and coaches. Proven technologies were combined in an intelligent manner and optimally matched with each other. All Euro 6 diesel vehicles feature a comprehensive efficient concept comprising needs-driven exhaust gas recirculation, diesel particulate filters and special exhaust gas aftertreatment.
Since June 2013, Audi has been producing a synthetic natural gas – Audi e-gas – and channeling it into the public network. The core element of the newly constructed plant in Lower Saxony is a methanation plant provided by MAN. The 16-meter high unit was designed and manufactured at MAN’s Deggendorf location. Using renewable power, the plant produces climate-neutral fuel that can be both saved and transported via the existing infrastructure.